Mood for Food
Food is more than just sustenance; it’s deeply intertwined with our emotions and moods. The phrase "mood for food" encapsulates how our feelings and mental states can influence our eating habits, cravings, and overall relationship with food. This article explores the psychological and emotional dimensions of food, examining how our moods shape our eating experiences and how food can, in turn, impact our emotional well-being.
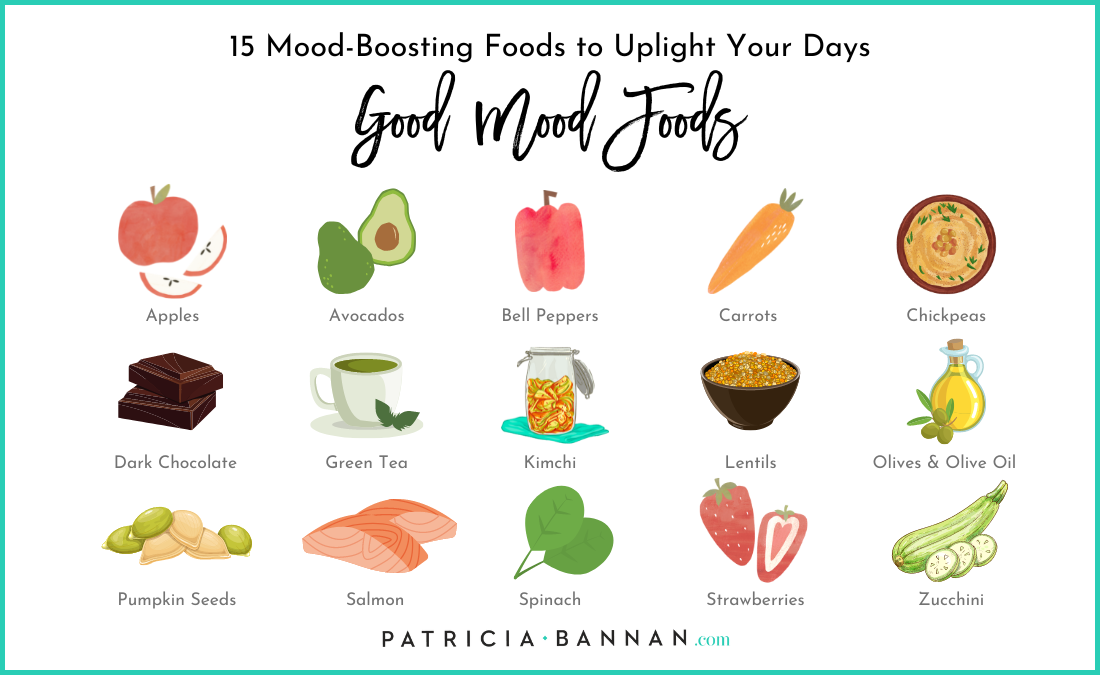
The Emotional Landscape of Eating
Our mood can significantly influence what we crave and how we eat. For instance:
Comfort Foods: When we're feeling down or stressed, we often turn to comfort foods. These are usually rich, hearty dishes that evoke a sense of nostalgia or warmth, such as macaroni and cheese or chocolate chip cookies. The appeal of comfort foods lies in their ability to provide immediate emotional relief and a sense of familiarity.
Celebratory Foods: Conversely, during times of celebration, we might crave foods that are indulgent or festive, like champagne, elaborate cakes, or gourmet dishes. These foods often represent joy and success and are enjoyed as part of our social rituals and celebrations.
How Moods Influence Food Choices
Different moods can lead to distinct eating patterns:
Stress and Anxiety: When stressed, people might seek out high-calorie, sugary, or fatty foods as a form of self-soothing. This phenomenon, sometimes referred to as “emotional eating,” can provide temporary comfort but may lead to long-term health consequences if not managed properly.
Happiness and Contentment: On the other hand, when we're happy, we might be more open to trying new foods or enjoying healthy options. Positive emotions can enhance our willingness to experiment with different flavors and cuisines, reflecting a more adventurous and open-minded approach to eating.
The Role of Food in Emotional Well-being
Food doesn't just reflect our moods; it can also play a role in shaping them:
Mood-Boosting Foods: Certain foods have been shown to positively influence mood. For example, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and walnuts, are linked to improved mood and cognitive function. Similarly, foods high in antioxidants, such as berries and leafy greens, can help reduce inflammation and support mental health.
Mindful Eating: Engaging in mindful eating practices—being fully present and attentive while eating—can help improve emotional well-being. By focusing on the sensory experience of eating, we can develop a healthier relationship with food and better understand our cravings and hunger signals.
Cultural and Personal Influences
Our cultural background and personal experiences also shape our mood for food:
Cultural Significance: Different cultures have unique foods associated with various emotional states and celebrations. For instance, in many Asian cultures, foods like congee or dumplings are traditionally eaten during times of illness or recovery, symbolizing comfort and nourishment.
Personal Preferences: Individual experiences and memories play a significant role in shaping our mood for food. A dish that brings comfort to one person might not have the same effect on another. Personal preferences and associations can deeply influence what we choose to eat in response to our emotional states.
Finding Balance
Understanding the connection between mood and food can help us make more mindful and balanced choices. Here are some tips for managing your mood for food:
Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body's hunger and fullness cues, and try to eat in response to genuine physical hunger rather than emotional cravings.
Choose Nutrient-Rich Foods: Opt for foods that nourish both your body and mind. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall well-being and help stabilize mood.
Practice Mindfulness: Engage in mindful eating practices to enhance your awareness of how different foods affect your mood and satisfaction. This can lead to more deliberate and satisfying eating experiences.
Conclusion
The mood for food is a multifaceted concept that highlights the deep connection between our emotions and eating habits. By exploring how our moods influence our food choices and understanding how food can impact our emotional state, we can develop a more balanced and mindful approach to eating. Whether seeking comfort or celebrating joy, our food choices reflect and shape our emotional landscape, making the exploration of this connection both fascinating and essential for overall well-being.
Post a Comment for "Mood for Food"